Have you noticed among the various field properties the 'Parent table', 'Parent ID field' and 'Parent caption field' properties?
To understand these properties we have to understand relationships.
A relationship is a condition imposed over a field that we shall call a
foreign key.
It means that any data value added to this foreign key field must exist in another field
that belongs to another table. The other field is called a
Parent ID field. The
table to which the parent ID field belongs is called a
Parent table.
Let's take an example ... suppose you have an orders table, in which you store information
about orders:
order_number,
order_date and
ordering_customer_number.
And suppose that you have another table in the database, the customers tables, which
stores information about customers:
customer_number,
customer_name,
customer_address and
customer_phone. We want to make sure that values in the ordering_customer_number field
of the orders table are always selected from existing values in the customer_number field
of the customers table.
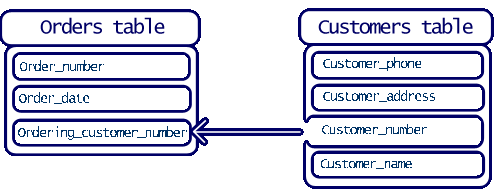
To satisfy this condition, we shall make the ordering_customer_number field of the orders table a
foreign key by specifying customers as its Parent table and customer_number as its Parent
ID field. Now whenever someone tries to add a value into the ordering_customer_number field, the
database will check to see if this value exists in the customer_number field or not.
If the database doesn't find a matching value, the added value will be rejected.
Note: The above explanation of a relationship is specific
to AppGini. To be more accurate, what we have explained as being a relationship should
rather be called a 'foreign key relationship'.
That's a pretty good question since its answer will highlight one of the unique
features of AppGini :)
MySQL database actually doesn't perform the above relationship check.
Despite their importance, foreign keys aren't implemented in MySQL (at least until
MySQL 3.23.31 which is the version I currently have).
But AppGini implements this
check and in a very powerful way. In the generated application, the ordering_customer_number field in the above example
will have a drop down menu listing all values found in its parent ID field, the customer_number.
The user can choose values only from this menu.
Moreover, if you specify a Parent Caption Field besides the parent ID field,
the menu will show values from another field of the parent table (for example, customer_name) but
store corresponding customer_number values. This makes the menu more understandable
because the user will see customer names instead of customer numbers, yet it is the
customer number that is stored in the foreign key field.
© Copyright 2002, BigProf Software. All rights reserved.

